Lipedema Fat vs. Normal Fat: Understanding the Key Differences
Are you struggling with disproportionate fat accumulation in your legs and arms that doesn’t seem to respond to diet and exercise? You may be wondering if it’s just stubborn fat or something more. Understanding the difference between lipedema fat vs. normal fat is crucial for proper diagnosis and management. This comprehensive guide will delve into the distinct characteristics of lipedema fat, how it differs from regular fat, and what you can do about it. We aim to provide you with the knowledge and resources needed to navigate this often misunderstood condition.
Unlike normal fat, lipedema fat is a chronic medical condition characterized by the abnormal buildup of fat cells, primarily in the legs, thighs, and arms. This fat is often painful to the touch and can lead to mobility issues, emotional distress, and other health complications. This article will explore the key distinctions between lipedema fat and normal fat, covering everything from cellular structure to treatment options. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of lipedema, empowering you to advocate for your health and well-being.
What is Lipedema and How Does it Differ from Obesity?
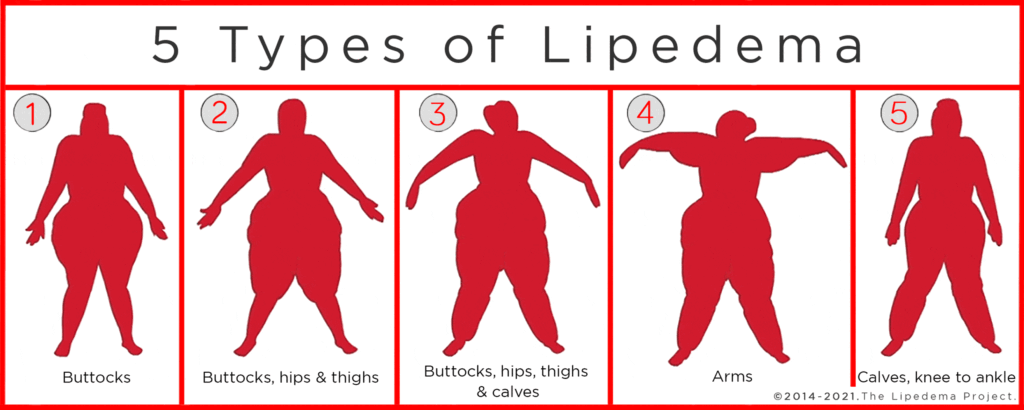
Lipedema is a chronic and progressive disorder characterized by the symmetrical buildup of fat in the subcutaneous tissue, primarily in the legs and arms. While obesity involves a general increase in fat throughout the body, lipedema fat accumulates in specific areas and is often resistant to diet and exercise. It’s important to note that lipedema can occur in individuals of all sizes, including those who are lean.
The key differences between lipedema and obesity extend beyond fat distribution. Lipedema fat is often painful, tender to the touch, and can cause swelling and bruising. Obesity, on the other hand, is typically not painful in the same way. Furthermore, lipedema is more common in women and is thought to be linked to hormonal changes, while obesity is influenced by a variety of factors, including genetics, diet, and lifestyle.
The Underlying Causes of Lipedema
The exact cause of lipedema is not fully understood, but it is believed to be a complex interplay of genetic, hormonal, and inflammatory factors. Research suggests that lipedema may be inherited, with a family history of the condition increasing the risk. Hormonal changes, such as those that occur during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause, are also thought to play a role in the development and progression of lipedema.
Inflammation is another key factor implicated in lipedema. Studies have shown that lipedema fat tissue exhibits signs of chronic inflammation, which can contribute to pain, swelling, and other symptoms. This inflammation may be triggered by various factors, including oxidative stress, immune system dysfunction, and alterations in the lymphatic system.
Stages of Lipedema Progression
Lipedema typically progresses through several stages, each characterized by increasing severity of symptoms. In Stage 1, the skin surface is smooth, and the fat tissue feels soft and spongy. As the condition progresses to Stage 2, the skin may develop a dimpled or orange-peel appearance, and the fat tissue becomes more firm and nodular. In Stage 3, large folds of skin and fat may develop, causing significant mobility issues and pain. Stage 4, also known as lipo-lymphedema, involves damage to the lymphatic system, leading to fluid buildup and swelling in addition to the fat accumulation.
Cellular Differences: What Makes Lipedema Fat Unique?
Lipedema fat cells differ from normal fat cells in several important ways. Studies have shown that lipedema fat cells are larger, more numerous, and less responsive to insulin than normal fat cells. This means that they are more likely to store fat and less likely to release it, contributing to the characteristic fat accumulation seen in lipedema.
Furthermore, lipedema fat cells exhibit altered metabolism and gene expression compared to normal fat cells. They produce more inflammatory molecules and less of certain hormones that regulate fat metabolism. These cellular differences contribute to the chronic inflammation and resistance to diet and exercise seen in lipedema.
The Role of Lymphatic System in Lipedema
The lymphatic system plays a crucial role in fluid balance, immune function, and fat metabolism. In lipedema, the lymphatic system can become impaired, leading to fluid buildup and swelling in the affected areas. This impairment can be caused by compression of lymphatic vessels by the excess fat tissue or by intrinsic abnormalities in the lymphatic system itself.
When the lymphatic system is not functioning properly, it can further exacerbate the symptoms of lipedema. The fluid buildup can cause pain, swelling, and heaviness in the legs and arms. It can also increase the risk of infections and skin breakdown. Therefore, maintaining lymphatic health is an important aspect of managing lipedema.
Diagnosing Lipedema: What to Expect
Diagnosing lipedema can be challenging, as it is often misdiagnosed as obesity or lymphedema. There is no single diagnostic test for lipedema, so diagnosis is typically based on a physical examination and a review of the patient’s medical history. Key diagnostic criteria include the symmetrical distribution of fat in the legs and arms, tenderness to the touch, and resistance to diet and exercise.
In some cases, imaging studies such as lymphoscintigraphy or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be used to assess the lymphatic system and rule out other conditions. However, these tests are not always necessary for diagnosis. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional who is knowledgeable about lipedema to receive an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
Ruling Out Other Conditions
Before diagnosing lipedema, it is important to rule out other conditions that can cause similar symptoms. These include lymphedema, which is characterized by swelling due to lymphatic system dysfunction; obesity, which involves a general increase in fat throughout the body; and venous insufficiency, which is a condition in which the veins in the legs do not properly return blood to the heart.
A thorough medical history, physical examination, and appropriate diagnostic tests can help differentiate lipedema from these other conditions. It is important to receive an accurate diagnosis in order to receive the most effective treatment.
Management and Treatment Options for Lipedema
While there is no cure for lipedema, there are several management and treatment options that can help improve symptoms and quality of life. These include conservative therapies such as compression therapy, manual lymphatic drainage, and exercise, as well as surgical options such as liposuction.
The specific treatment plan will depend on the individual’s symptoms, stage of lipedema, and overall health. It is important to work with a healthcare professional who is knowledgeable about lipedema to develop a personalized treatment plan.
Conservative Therapies for Lipedema
Conservative therapies are the mainstay of lipedema management. Compression therapy involves wearing compression garments to help reduce swelling and improve lymphatic drainage. Manual lymphatic drainage is a gentle massage technique that helps to move fluid out of the affected areas.
Exercise is also an important part of lipedema management. Low-impact exercises such as swimming, walking, and cycling can help to improve circulation, reduce swelling, and maintain mobility. It is important to avoid high-impact exercises that can put stress on the joints.
Surgical Options: Liposuction for Lipedema
Liposuction can be an effective treatment option for lipedema, particularly for individuals with advanced stages of the condition. Liposuction involves removing excess fat tissue from the affected areas, which can help to reduce pain, swelling, and improve mobility. However, it is important to choose a surgeon who is experienced in treating lipedema, as traditional liposuction techniques can damage the lymphatic system.
Water-assisted liposuction (WAL) and tumescent liposuction are two techniques that are considered to be safer for individuals with lipedema. These techniques use a gentle stream of fluid to dislodge the fat cells, minimizing damage to the surrounding tissues.
The Importance of Early Diagnosis and Intervention
Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial for managing lipedema and preventing its progression. The earlier lipedema is diagnosed, the sooner treatment can be initiated, which can help to slow the progression of the disease and improve symptoms. Early intervention can also help to prevent complications such as lymphedema and mobility issues.
If you suspect that you may have lipedema, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional who is knowledgeable about the condition. An accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan can make a significant difference in your quality of life.
The Emotional and Psychological Impact of Lipedema
Lipedema can have a significant emotional and psychological impact on individuals. The chronic pain, swelling, and disfigurement associated with lipedema can lead to feelings of frustration, anxiety, and depression. Many individuals with lipedema also experience body image issues and social isolation.
It is important to address the emotional and psychological aspects of lipedema in addition to the physical symptoms. Support groups, counseling, and therapy can be helpful for individuals with lipedema to cope with the emotional challenges of the condition.
The Future of Lipedema Research and Treatment
Research into lipedema is ongoing, with the goal of better understanding the causes of the condition and developing more effective treatments. Current research is focused on identifying the genes that contribute to lipedema, investigating the role of inflammation and the lymphatic system, and developing new therapies that target the underlying mechanisms of the disease.
As research progresses, it is hoped that more effective treatments for lipedema will become available, improving the lives of individuals affected by this condition.
Expert Insight: The Ketogenic Diet and Lipedema Management
While not a cure, some experts believe that a ketogenic diet may offer benefits for managing lipedema symptoms. A ketogenic diet, high in fat and low in carbohydrates, forces the body to burn fat for fuel, potentially reducing inflammation and promoting weight loss. A registered dietitian specializing in lipedema can provide personalized guidance. It’s important to note that this is one potential tool and should be approached with expert advice.
Understanding Lipedema Fat and Taking Control of Your Health
Understanding the differences between lipedema fat vs. normal fat is the first step toward taking control of your health and well-being. Lipedema is a complex condition that requires a comprehensive and individualized approach to management. By working with a healthcare professional who is knowledgeable about lipedema, you can develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses your specific symptoms and needs.
Remember, you are not alone. There are many resources available to support you on your journey with lipedema. Join a support group, connect with other individuals with lipedema, and advocate for your health. By working together, we can raise awareness of lipedema and improve the lives of those affected by this condition. If you’re ready to explore treatment options tailored to your specific needs, contact our specialists today for a personalized consultation.
