How Long Do Bed Bugs Live? Understanding Their Lifespan and Behavior
Discovering bed bugs in your home is a nightmare. These tiny pests can cause itchy bites, sleepless nights, and significant anxiety. A common question that arises when dealing with a bed bug infestation is: how long do bed bugs live? Understanding the bed bug lifespan is crucial for effective treatment and prevention. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of the bed bug life cycle, factors influencing their longevity, and expert strategies for eliminating these resilient pests. We aim to provide you with the most up-to-date, reliable information, drawing from entomological research and practical pest control experience to help you reclaim your home.
The Bed Bug Life Cycle: From Egg to Adult
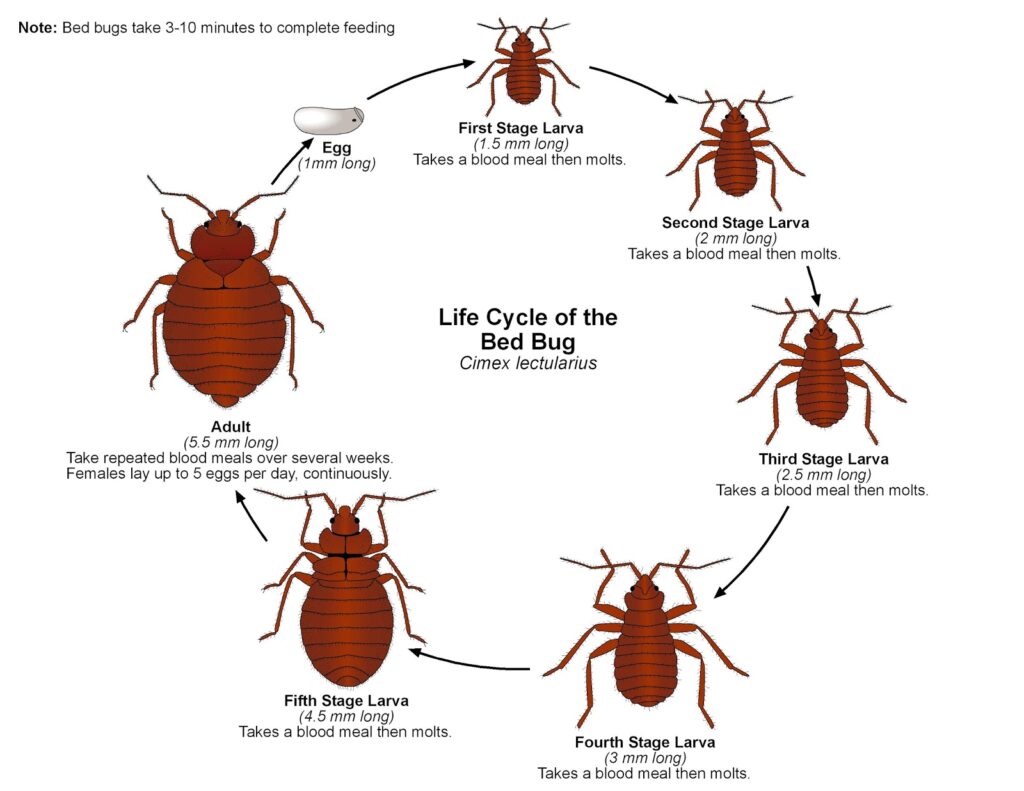
The lifespan of a bed bug is intricately linked to its life cycle, which consists of several distinct stages. Understanding these stages is essential for targeting the most vulnerable points in their development and implementing effective control measures.
Egg Stage
Bed bug eggs are tiny, pearly white, and about 1mm in length. They are typically laid in cracks and crevices near where people sleep. A female bed bug can lay several eggs per day, potentially hundreds in her lifetime. The eggs usually hatch within 6 to 17 days, depending on environmental conditions such as temperature and humidity.
Nymph Stage
Once hatched, bed bugs enter the nymph stage. Nymphs are essentially miniature versions of adult bed bugs. They go through five nymphal stages, each requiring a blood meal to molt and progress to the next stage. The nymph stage is when bed bugs are most vulnerable due to their reliance on frequent feeding. The duration of each nymphal stage depends on access to blood meals and environmental factors, but it generally takes several weeks to a few months to complete all five stages.
Adult Stage
After the fifth molt, the bed bug reaches adulthood. Adult bed bugs are reddish-brown, flattened, and about 4-5mm long. They can survive for several months without feeding, although they prefer to feed regularly. A well-fed adult female will continue to lay eggs, perpetuating the infestation. Understanding that how long do bed bugs live as adults depends heavily on environmental conditions and food availability is key to controlling infestations.
Factors Influencing Bed Bug Lifespan
Several factors influence how long bed bugs live, including temperature, humidity, food availability, and access to suitable harborage sites. Understanding these factors can help you create an environment less conducive to bed bug survival.
Temperature
Temperature plays a crucial role in bed bug development and survival. Bed bugs thrive in warm environments, typically between 70°F and 80°F (21°C and 27°C). Lower temperatures can slow down their metabolism and prolong their life cycle. Extreme temperatures, both hot and cold, can be lethal. For instance, exposure to temperatures above 120°F (49°C) or below 0°F (-18°C) for a sustained period can kill bed bugs.
Humidity
Humidity also affects bed bug survival. Bed bugs prefer moderate to high humidity levels. Low humidity can dehydrate them and shorten their lifespan. Maintaining optimal humidity levels in your home can help prevent bed bugs from thriving.
Food Availability
Bed bugs are obligate blood feeders, meaning they require blood to survive and reproduce. The availability of blood meals directly impacts how long bed bugs live. Without regular access to blood, bed bugs can enter a state of dormancy and survive for extended periods, sometimes several months. This resilience makes them particularly challenging to eradicate.
Harborage Sites
Bed bugs prefer dark, secluded harborage sites close to their hosts. These sites include cracks and crevices in mattresses, bed frames, furniture, and walls. The availability of suitable harborage sites can influence bed bug survival by providing protection from predators and environmental stressors.
How Long Can Bed Bugs Live Without Feeding?
One of the most concerning aspects of bed bugs is their ability to survive for extended periods without feeding. This resilience makes them difficult to eradicate and can lead to persistent infestations. The exact duration a bed bug can survive without food depends on its life stage and environmental conditions.
Nymphs
Nymphs are more vulnerable to starvation than adults. They typically need to feed every few days to molt and progress to the next stage. Without a blood meal, nymphs can survive for a few weeks to a couple of months, depending on temperature and humidity.
Adults
Adult bed bugs are much more resilient. They can survive for several months without feeding, especially in cooler temperatures. Some studies have shown that adult bed bugs can survive for up to a year without a blood meal under optimal conditions. This remarkable ability to withstand starvation makes them particularly challenging to eliminate.
Bed Bug Detection: Identifying an Infestation Early
Early detection is key to preventing a full-blown bed bug infestation. Regular inspections of your home, especially sleeping areas, can help you identify bed bugs before they become a major problem.
Visual Inspection
Carefully inspect your mattress, bed frame, and surrounding furniture for signs of bed bugs. Look for live bed bugs, shed skins, fecal spots (small, dark stains), and eggs. Pay close attention to seams, tufts, and crevices where bed bugs like to hide.
Bed Bug Monitors
Bed bug monitors are devices designed to attract and trap bed bugs. These monitors can be placed under furniture legs or near sleeping areas to detect bed bug activity. While monitors can be helpful, they are not always reliable, as bed bugs may not always be attracted to them.
Professional Inspection
If you suspect a bed bug infestation but are unable to find any evidence, consider hiring a professional pest control company to conduct a thorough inspection. Professionals have the training and tools to detect bed bugs in even the most hidden locations.
Effective Bed Bug Treatment Strategies
Once you’ve confirmed a bed bug infestation, it’s essential to implement effective treatment strategies to eliminate these pests. A combination of methods is often necessary to achieve complete eradication.
Heat Treatment
Heat treatment involves raising the temperature of the infested area to a lethal level for bed bugs. Professional heat treatment services use specialized equipment to heat the entire room to around 120°F (49°C) for several hours. This method is highly effective, as it kills bed bugs at all life stages, including eggs.
Chemical Treatment
Chemical treatment involves applying insecticides to infested areas. Various insecticides are available, including pyrethrins, pyrethroids, and desiccants. It’s important to use insecticides specifically labeled for bed bug control and to follow the instructions carefully. Multiple treatments may be necessary to eliminate all bed bugs.
Steam Treatment
Steam treatment involves using a steamer to apply hot steam to infested areas. The steam penetrates cracks and crevices, killing bed bugs on contact. Steam treatment is a good option for treating mattresses, furniture, and other sensitive items that cannot be treated with chemicals.
Vacuuming
Vacuuming can help remove bed bugs, eggs, and shed skins from infested areas. Use a vacuum with a HEPA filter to prevent allergens from being released into the air. Vacuum thoroughly along seams, tufts, and crevices of mattresses, furniture, and carpets. Dispose of the vacuum bag or empty the canister into a sealed plastic bag immediately after vacuuming.
Encasements
Mattress and box spring encasements are zippered covers that completely enclose the mattress and box spring, preventing bed bugs from entering or escaping. Encasements are a good option for protecting your mattress from infestation and for trapping any existing bed bugs inside.
Preventing Bed Bug Infestations: Proactive Measures
Prevention is always better than cure when it comes to bed bugs. Taking proactive measures can help you avoid infestations and protect your home.
Inspect Secondhand Items
Before bringing any secondhand furniture, mattresses, or clothing into your home, carefully inspect them for signs of bed bugs. Pay close attention to seams, tufts, and crevices.
Use Luggage Racks
When traveling, use luggage racks to keep your luggage off the floor and away from beds. This can help prevent bed bugs from hitchhiking a ride back to your home.
Seal Cracks and Crevices
Seal any cracks and crevices in your walls, floors, and furniture to eliminate potential harborage sites for bed bugs.
Regular Cleaning
Regularly vacuum and clean your home to remove dust, debris, and potential food sources for bed bugs.
The Role of Professional Pest Control
While DIY bed bug treatments can be effective in some cases, professional pest control services are often necessary to eradicate severe infestations. Professional pest control companies have the training, experience, and tools to effectively eliminate bed bugs and prevent future infestations. They can also provide valuable advice on how to prevent bed bugs from returning.
Beyond the Bite: The Psychological Impact of Bed Bugs
The presence of bed bugs extends beyond just physical discomfort. Many individuals experience significant psychological distress due to infestations. The constant itching, anxiety about being bitten, and the social stigma associated with bed bugs can lead to insomnia, depression, and even feelings of paranoia. Addressing both the physical and psychological aspects of a bed bug infestation is crucial for overall well-being.
According to entomologist Dr. Harold Harlan, a leading expert on bed bugs, “The psychological impact of bed bug infestations is often underestimated. People can experience significant stress and anxiety, which can affect their quality of life.”
Debunking Common Myths About Bed Bugs
Many misconceptions surround bed bugs, which can hinder effective prevention and treatment. Let’s debunk some common myths:
- Myth: Bed bugs are a sign of poor hygiene. Fact: Bed bugs are attracted to warmth, carbon dioxide, and blood, not dirt or filth. They can infest even the cleanest homes.
- Myth: Bed bugs only live in beds. Fact: While bed bugs are commonly found in beds, they can also infest furniture, walls, and other areas of the home.
- Myth: You can’t see bed bugs. Fact: Adult bed bugs are visible to the naked eye, although they are small and can be difficult to spot.
- Myth: Bed bugs transmit diseases. Fact: Bed bugs are not known to transmit any diseases to humans.
Expert Advice for Long-Term Bed Bug Management
Long-term bed bug management requires a multi-faceted approach that combines prevention, early detection, and effective treatment. Here are some expert tips for keeping bed bugs at bay:
- Regular Inspections: Conduct regular inspections of your home, especially sleeping areas, to detect bed bugs early.
- Protective Measures: Use mattress and box spring encasements to protect your bed from infestation.
- Travel Precautions: Take precautions when traveling to avoid bringing bed bugs back to your home.
- Professional Assistance: Don’t hesitate to seek professional help if you suspect a bed bug infestation.
Understanding the Bed Bug’s Adaptability for Effective Control
Bed bugs are incredibly adaptable creatures, which contributes to their resilience and makes them difficult to eradicate. Their ability to survive for extended periods without feeding, their rapid reproduction rate, and their tendency to hide in secluded harborage sites all contribute to their success. Understanding these adaptations is crucial for developing effective control strategies.
The Future of Bed Bug Control: Emerging Technologies
The field of bed bug control is constantly evolving, with new technologies and approaches being developed all the time. Some emerging technologies include:
- Improved Insecticides: Researchers are working on developing new insecticides that are more effective against bed bugs and less harmful to humans and the environment.
- Smart Traps: Smart traps use sensors and data analysis to detect bed bug activity and provide real-time information to pest control professionals.
- Biological Control: Biological control involves using natural enemies of bed bugs, such as fungi or nematodes, to control populations.
Reclaiming Your Home and Peace of Mind
Dealing with a bed bug infestation can be a stressful and overwhelming experience. By understanding the bed bug life cycle, implementing effective treatment strategies, and taking proactive prevention measures, you can reclaim your home and peace of mind. Remember, early detection and professional assistance are key to successfully eradicating bed bugs and preventing future infestations.
Protecting Your Home from Bed Bugs
Knowing how long do bed bugs live and understanding their behavior can dramatically improve your chances of successfully eliminating them. From understanding their life cycle to implementing preventative measures, every step contributes to a bed bug-free environment. If you suspect an infestation, act quickly and consider consulting with pest control professionals for a comprehensive solution. By staying informed and proactive, you can protect your home and ensure restful nights.
