Do Bed Bugs Live in Hair? Separating Fact from Fiction
Finding an itchy bite can send anyone spiraling, especially when the possibility of bed bugs enters the picture. The immediate question that often pops up is: “Do bed bugs live in hair?” It’s a common concern, and understanding the truth is crucial for effective prevention and treatment. This comprehensive guide will delve into the realities of bed bugs and their relationship with human hair, providing expert insights to help you identify, address, and prevent infestations. We’ll cover everything from identifying potential symptoms to implementing effective strategies for eliminating these unwelcome guests.
Unlike lice, which are specifically adapted to live and breed in human hair, bed bugs are primarily interested in one thing: blood. Their flat bodies allow them to hide in tiny cracks and crevices, emerging at night to feed on unsuspecting sleepers. While they might occasionally crawl through hair to reach the skin, they don’t typically nest or live there. Think of human hair as a temporary bridge rather than a permanent home.
Understanding Bed Bugs and Their Behavior
Bed bugs (Cimex lectularius) are small, nocturnal insects that feed on human blood. They are reddish-brown in color, about the size of an apple seed, and have a flat, oval shape. These pests are notorious for their ability to infest homes, hotels, and other dwellings, causing itchy bites and considerable anxiety. Understanding their behavior is the first step in preventing and addressing infestations. Their capacity to hide in very small spaces is what makes them so difficult to eradicate.
Bed Bug Habitats
Bed bugs prefer dark, secluded environments close to their food source. Mattresses, box springs, bed frames, and headboards are their prime real estate. However, they can also be found in other areas, including:
- Cracks in walls and floors
- Behind wallpaper
- Inside furniture
- Under carpets
- Within electrical outlets
Their adaptability allows them to thrive in various conditions, making early detection and comprehensive treatment essential. Regular inspections of these areas can help identify infestations before they become widespread.
Feeding Habits
Bed bugs are primarily active at night, when they emerge from their hiding places to feed on sleeping humans. They use their piercing-sucking mouthparts to draw blood, typically feeding for about 3-10 minutes until they are engorged. After feeding, they retreat to their hiding places to digest their meal. This cycle continues until they are discovered and eliminated.
The bites themselves are usually painless at first, but they can develop into itchy welts or red bumps within a few hours or days. The delayed reaction is due to the body’s immune response to the bed bug’s saliva, which contains an anticoagulant.
The Truth About Bed Bugs and Hair
The common misconception that bed bugs live in hair likely stems from confusion with other pests like lice. While bed bugs may occasionally crawl through hair to reach the skin, they do not establish themselves there. Here’s why:
- Lack of Sustenance: Bed bugs feed on blood, not skin cells or hair follicles. Hair does not provide them with any nutritional value.
- Unsuitable Environment: Human hair is not conducive to nesting or breeding. Bed bugs prefer dark, sheltered environments like mattresses and furniture.
- Grooming Habits: Regular grooming habits, such as combing and washing hair, would disrupt any attempt by bed bugs to establish themselves in hair.
In our experience, people often mistake other skin conditions or insect bites for bed bug infestations in their hair. It’s crucial to accurately identify the source of the problem to ensure effective treatment.
Why the Confusion?
Several factors contribute to the confusion about bed bugs and hair:
- Similarity to Lice: Lice are known to live and breed in hair, leading some people to assume that bed bugs do the same.
- Proximity to the Head: Bed bugs often bite areas of the body that are exposed during sleep, including the face, neck, and arms, which are close to the head and hair.
- Anxiety and Misinterpretation: The anxiety caused by bed bug infestations can lead people to misinterpret other symptoms, such as scalp irritation or dandruff, as signs of bed bugs in hair.
Identifying Symptoms of Bed Bugs
While bed bugs don’t live in hair, understanding the signs of a bed bug infestation is crucial. The most common symptom is the presence of itchy bites, but other indicators can help confirm an infestation.
Common Signs of Bed Bug Infestation
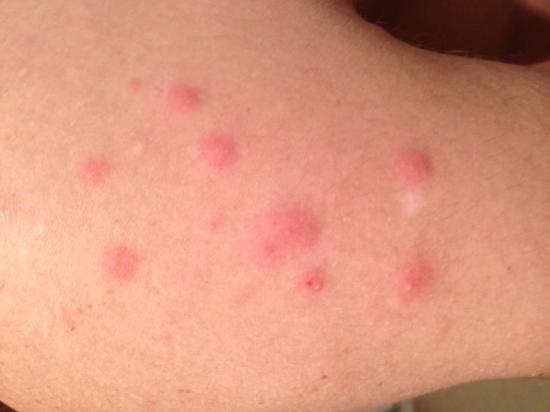
- Bite Marks: Red, itchy welts or bumps on the skin, often appearing in clusters or lines. These bites are commonly found on areas of the body exposed during sleep, such as the face, neck, arms, and hands.
- Blood Stains: Small blood stains on bedding, mattresses, or furniture. These stains occur when bed bugs are crushed after feeding.
- Fecal Spots: Dark, rusty-colored spots on bedding, mattresses, or walls. These spots are bed bug excrement and are a clear sign of infestation.
- Shed Skins: Pale, translucent skins shed by bed bugs as they grow. These skins are often found in areas where bed bugs hide.
- Live Bed Bugs: Actual sightings of live bed bugs. They are typically found in their hiding places, such as mattresses, bed frames, and furniture.
Differentiating Bed Bug Bites from Other Bites
Bed bug bites can often be confused with bites from other insects, such as mosquitoes, fleas, or spiders. Here are some key differences to help you distinguish them:
- Appearance: Bed bug bites are typically small, red welts that appear in clusters or lines. Mosquito bites are usually larger and more isolated. Flea bites are often found around the ankles and lower legs.
- Itchiness: Bed bug bites can be intensely itchy, but the level of itchiness can vary from person to person. Some people may not react to the bites at all.
- Timing: Bed bug bites usually appear a few hours or days after being bitten. Mosquito bites are typically immediate.
- Location: Bed bug bites are commonly found on areas of the body exposed during sleep, such as the face, neck, arms, and hands. Flea bites are often found around the ankles and lower legs.
If you are unsure whether you have bed bug bites, it is best to consult with a healthcare professional or pest control expert.
Treating Bed Bug Bites and Infestations
Treating bed bug bites and infestations requires a multi-faceted approach. While the bites themselves can be managed with over-the-counter remedies, eliminating the infestation requires more comprehensive measures.
Treating Bed Bug Bites
Bed bug bites can be itchy and uncomfortable, but they usually resolve on their own within a week or two. Here are some ways to relieve the symptoms:
- Wash the Bites: Wash the bites with soap and water to prevent infection.
- Apply Anti-Itch Cream: Apply an over-the-counter anti-itch cream, such as hydrocortisone or calamine lotion, to relieve itching.
- Take Antihistamines: Take an oral antihistamine to reduce itching and inflammation.
- Avoid Scratching: Avoid scratching the bites, as this can lead to infection.
In rare cases, bed bug bites can cause a severe allergic reaction. If you experience symptoms such as difficulty breathing, swelling, or hives, seek immediate medical attention.
Eliminating Bed Bug Infestations
Eliminating a bed bug infestation can be challenging, but it is possible with the right approach. Here are some effective strategies:
- Professional Pest Control: Hiring a professional pest control company is often the most effective way to eliminate a bed bug infestation. Pest control experts have the knowledge, experience, and tools to identify and treat infestations thoroughly.
- Thorough Cleaning: Wash all bedding, linens, and clothing in hot water and dry them on high heat. Vacuum mattresses, carpets, and furniture thoroughly.
- Seal Cracks and Crevices: Seal any cracks and crevices in walls, floors, and furniture to eliminate hiding places for bed bugs.
- Use Mattress Encasements: Encase mattresses and box springs in bed bug-proof encasements to prevent bed bugs from entering or escaping.
- Insecticides: Use insecticides specifically designed for bed bugs. Follow the instructions carefully and use them in conjunction with other treatment methods.
It is important to be persistent and thorough when treating a bed bug infestation. It may take multiple treatments to completely eliminate the pests. Based on expert consensus, a combination of professional pest control and diligent home treatment is often the most effective approach.
Preventing Bed Bug Infestations
Prevention is key when it comes to bed bugs. Taking proactive measures can significantly reduce your risk of infestation.
Tips for Preventing Bed Bug Infestations
- Inspect Secondhand Items: Thoroughly inspect secondhand furniture, mattresses, and clothing before bringing them into your home.
- Be Vigilant When Traveling: When traveling, inspect hotel rooms for signs of bed bugs. Check mattresses, bedding, and furniture for blood stains, fecal spots, and live bed bugs.
- Use Luggage Racks: Keep luggage off the floor and use luggage racks to prevent bed bugs from crawling into your belongings.
- Wash Clothes After Traveling: Wash all clothing after traveling, even if you didn’t wear it.
- Seal Cracks and Crevices: Seal any cracks and crevices in walls, floors, and furniture to eliminate hiding places for bed bugs.
- Regular Inspections: Regularly inspect your home for signs of bed bugs, especially in areas where they are likely to hide.
Bed Bug Barriers: A Proactive Defense
Bed bug barriers are physical or chemical measures taken to prevent bed bugs from infesting a specific area. These barriers can be particularly useful in homes, hotels, and other places where bed bug infestations are a concern. One of the most effective bed bug barriers is a mattress encasement. These encasements are designed to completely seal off the mattress, preventing bed bugs from entering or escaping. They are made of a durable, bed bug-proof material that is resistant to punctures and tears. Mattress encasements are easy to install and maintain, making them a popular choice for preventing bed bug infestations.
The Role of Diatomaceous Earth
Diatomaceous earth (DE) is a natural substance made from the fossilized remains of diatoms, a type of algae. It is a fine, powdery substance that is used as an insecticide. DE works by absorbing the waxy outer layer of insects, causing them to dehydrate and die. Diatomaceous earth is safe for humans and pets when used as directed, making it a popular choice for controlling bed bugs. To use DE to prevent bed bugs, sprinkle a thin layer of DE around the perimeter of your bed, along baseboards, and in other areas where bed bugs are likely to travel. Be sure to use food-grade DE, as other types of DE can be harmful. DE is a slow-acting insecticide, so it may take several days or weeks to see results. However, it is a safe and effective way to control bed bugs.
Understanding Bed Bug Sprays
Bed bug sprays are insecticides specifically designed to kill bed bugs. They come in a variety of formulations, including aerosols, liquids, and dusts. Bed bug sprays work by either killing bed bugs on contact or by leaving a residual effect that kills bed bugs when they come into contact with the treated surface. When using bed bug sprays, it is important to follow the instructions carefully and to use them in conjunction with other treatment methods. Spray all areas where bed bugs are likely to hide, including mattresses, bed frames, baseboards, and furniture.
Beyond the Bite: Addressing the Psychological Impact
Dealing with a bed bug infestation extends beyond the physical symptoms of bites. The psychological impact can be significant, leading to anxiety, stress, and even sleep disturbances. Many individuals report feeling constantly on edge, fearing the next bite. This can disrupt daily routines and affect overall quality of life. It’s crucial to acknowledge and address these emotional challenges. Seeking support from friends, family, or a therapist can be beneficial in managing the stress and anxiety associated with bed bug infestations. Remember, you’re not alone, and there are resources available to help you cope with both the physical and emotional aspects of dealing with these pests.
Final Thoughts on Bed Bug Prevention
While the idea of bed bugs infesting your hair can be unsettling, it’s important to remember that they primarily target skin for feeding and do not live in hair. Understanding their behavior, identifying the signs of infestation, and implementing effective prevention and treatment strategies are crucial for keeping these pests at bay. By staying informed and proactive, you can protect your home and your peace of mind. If you suspect a bed bug infestation, don’t hesitate to consult with a pest control professional for expert guidance and treatment. Share your experiences with bed bug prevention in the comments below.
