Decoding Positive ANA and ICD-10: A Comprehensive Guide
Navigating the world of autoimmune diseases and diagnostic codes can feel overwhelming, especially when faced with terms like “positive ANA” and “ICD-10.” This comprehensive guide aims to demystify these concepts, providing a clear understanding of what a positive Antinuclear Antibody (ANA) test means in the context of ICD-10 coding. We will explore the significance of a positive ANA ICD 10, what it indicates about potential health conditions, and how healthcare professionals use this information for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning. Our goal is to empower you with knowledge, offering insights into the complexities of autoimmune diagnostics and coding.
Understanding Antinuclear Antibodies (ANA)
Antinuclear antibodies (ANAs) are autoantibodies that bind to components within the cell nucleus. The presence of ANAs in the blood can be an indicator of an autoimmune disorder, where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own tissues. However, it’s crucial to understand that a positive ANA test doesn’t automatically mean you have an autoimmune disease. Many healthy individuals can have positive ANA results, albeit often at lower titers.
The ANA test is typically performed using a technique called indirect immunofluorescence assay (IFA). A blood sample is taken, and the serum is diluted and applied to cells fixed on a slide. If ANAs are present in the serum, they will bind to the nuclear antigens in the cells. A fluorescently labeled antibody is then added, which binds to the ANAs, making them visible under a microscope. The pattern and intensity of the fluorescence are noted, providing information about the type and amount of ANAs present.
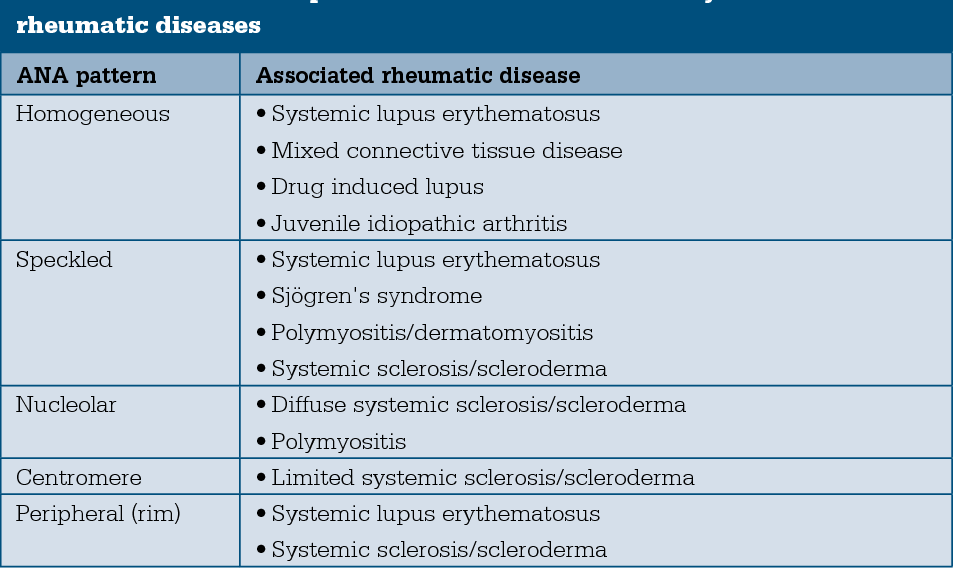
ANA Patterns and Their Significance
The pattern of fluorescence observed during the ANA test can provide clues about the specific autoimmune disease that might be present. Common ANA patterns include:
- Homogeneous: Often associated with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and drug-induced lupus.
- Speckled: Can be seen in SLE, Sjogren’s syndrome, scleroderma, and mixed connective tissue disease (MCTD).
- Nucleolar: Suggestive of scleroderma.
- Centromere: Strongly associated with CREST syndrome (a limited form of scleroderma).
It’s important to note that these patterns are not definitive diagnoses but rather provide additional information that helps guide further investigations.
Factors Affecting ANA Results
Several factors can influence ANA test results, including age, sex, and certain medications. The prevalence of positive ANAs increases with age, and women are more likely to have positive results than men. Some medications, such as hydralazine and procainamide, are known to induce a lupus-like syndrome and can cause a positive ANA.
ICD-10 Coding: The Language of Medical Diagnosis
The International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision (ICD-10), is a globally recognized system used to classify and code diseases, signs and symptoms, abnormal findings, complaints, social circumstances, and external causes of injury or diseases. In the United States, ICD-10 is used for diagnostic coding in healthcare settings. ICD-10 codes are crucial for accurate billing, data analysis, and tracking disease prevalence.
ICD-10 codes are alphanumeric, consisting of a letter followed by two or more numbers. The first letter generally indicates the broad category of the disease or condition. For example, codes starting with ‘M’ often relate to diseases of the musculoskeletal system and connective tissue, which are frequently associated with positive ANA results.
The Role of ICD-10 in Autoimmune Disease Diagnosis
When a patient presents with symptoms suggestive of an autoimmune disease and has a positive ANA test, healthcare providers use ICD-10 codes to document the patient’s condition and the diagnostic tests performed. The specific ICD-10 code used will depend on the suspected or confirmed diagnosis. The positive ANA result itself does not have a direct ICD-10 code; instead, the codes reflect the underlying condition or the signs and symptoms being investigated.
Linking Positive ANA to Relevant ICD-10 Codes
A positive ANA result is often a starting point in the diagnostic process, leading to further investigations to identify the underlying cause. Here are some examples of ICD-10 codes that may be relevant in the context of a positive ANA:
- M32.9: Systemic lupus erythematosus, unspecified – Used when SLE is suspected or confirmed, but the specific type is not specified.
- M35.0: Sicca syndrome [Sjogren’s] – Used when Sjogren’s syndrome is suspected or confirmed.
- M34.0: Progressive systemic sclerosis [Scleroderma] – Used when scleroderma is suspected or confirmed.
- M35.1: Other overlap syndromes – Used when the patient has features of more than one autoimmune disease.
- M05-M06: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Used when Rheumatoid Arthritis is suspected or confirmed.
It’s important to remember that the ICD-10 code should accurately reflect the patient’s condition based on clinical evaluation, laboratory findings, and other diagnostic tests. A positive ANA result is just one piece of the puzzle.
The Diagnostic Journey: From Positive ANA to Diagnosis
When a patient tests positive for ANA, the healthcare provider will typically take a detailed medical history, perform a physical examination, and order additional laboratory tests to determine the cause of the positive result. These tests may include:
- Specific antibody tests: These tests look for antibodies associated with specific autoimmune diseases, such as anti-dsDNA (SLE), anti-Ro/SSA (Sjogren’s syndrome), and anti-Scl-70 (scleroderma).
- Inflammatory markers: Tests such as erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and C-reactive protein (CRP) can help assess the level of inflammation in the body.
- Complete blood count (CBC): This test measures the different types of blood cells and can help identify abnormalities that may be associated with autoimmune diseases.
- Urinalysis: This test can help detect kidney involvement, which is common in some autoimmune diseases.
The results of these tests, along with the patient’s symptoms and medical history, will help the healthcare provider arrive at a diagnosis. In some cases, a diagnosis may not be possible immediately, and the patient may need to be monitored over time.
The Importance of Accurate ICD-10 Coding
Accurate ICD-10 coding is essential for several reasons:
- Proper billing and reimbursement: ICD-10 codes are used to bill insurance companies for medical services. Incorrect coding can lead to claim denials or delays in payment.
- Data analysis and research: ICD-10 codes are used to track disease prevalence and trends. Accurate coding is essential for public health surveillance and research.
- Quality improvement: ICD-10 codes can be used to monitor the quality of healthcare services. By tracking the outcomes of patients with specific diagnoses, healthcare providers can identify areas for improvement.
Healthcare providers and coders must stay up-to-date with the latest ICD-10 coding guidelines to ensure accuracy.
Navigating the Complexities of Autoimmune Disease
Autoimmune diseases are complex and can be challenging to diagnose. A positive ANA test is just one piece of the puzzle. It’s important to work closely with your healthcare provider to understand your test results and develop a personalized treatment plan. Early diagnosis and treatment can help improve outcomes and quality of life for people with autoimmune diseases.
Expert Insights on Managing Autoimmune Conditions
Managing autoimmune conditions often involves a multidisciplinary approach, incorporating medication, lifestyle modifications, and supportive therapies. Leading experts in rheumatology emphasize the importance of:
- Medication adherence: Taking medications as prescribed is crucial for controlling inflammation and preventing disease progression.
- Regular exercise: Exercise can help improve muscle strength, reduce pain, and boost energy levels.
- Healthy diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help support the immune system and reduce inflammation.
- Stress management: Stress can exacerbate autoimmune symptoms. Techniques such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing can help manage stress levels.
- Regular monitoring: Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider are essential for monitoring disease activity and adjusting treatment as needed.
Real-World Value: Empowering Patients with Knowledge
Understanding the nuances of a positive ANA test and its connection to ICD-10 coding empowers patients to actively participate in their healthcare journey. By being informed about their condition and the diagnostic process, patients can:
- Ask informed questions: Patients who understand their test results are better equipped to ask relevant questions and engage in meaningful discussions with their healthcare providers.
- Advocate for themselves: Knowledge empowers patients to advocate for their needs and ensure they receive appropriate care.
- Make informed decisions: Understanding the potential implications of a positive ANA test allows patients to make informed decisions about their treatment options.
Our goal is to provide you with the information you need to navigate the complexities of autoimmune disease with confidence.
Beyond the Basics: Advanced Considerations for Positive ANA
While a positive ANA test is a significant indicator, several advanced considerations come into play during diagnosis and treatment. For instance, the titer (the concentration of antibodies) and the pattern of the ANA can provide clues, but they are not definitive. A high titer doesn’t always mean a more severe disease, and some individuals with autoimmune diseases may have low or even negative ANA results.
Furthermore, the clinical context is paramount. A positive ANA in someone with classic symptoms of lupus is far more significant than a positive ANA in an otherwise healthy individual. The physician must correlate the lab findings with the patient’s clinical presentation to arrive at an accurate diagnosis. In our experience, a thorough evaluation, including a detailed medical history and physical examination, is crucial.
Reviewing Key Takeaways and Moving Forward
In summary, a positive ANA test is a finding that warrants further investigation but does not automatically equate to an autoimmune disease diagnosis. The appropriate ICD-10 code will reflect the underlying condition or the signs and symptoms being investigated, based on a comprehensive clinical evaluation. We hope this guide has provided you with a clearer understanding of the relationship between a positive ANA ICD 10 and the broader context of autoimmune diagnostics. If you have concerns about your ANA results, we encourage you to consult with a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and support.
