Decoding Generations: A Comprehensive Guide by Year
Have you ever wondered why people from different age groups seem to see the world so differently? A key to understanding these varying perspectives lies in the concept of “generation by year.” This isn’t just about assigning labels; it’s about recognizing the shared experiences, cultural touchstones, and formative events that shape the values, beliefs, and behaviors of individuals born within a specific timeframe. This comprehensive guide will explore the nuances of generational cohorts, offering insights into their defining characteristics and how they impact society, the workplace, and even marketing strategies. We’ll delve into the historical context, technological advancements, and societal shifts that have shaped each generation, providing a deeper understanding of the forces that mold our world.
What is a Generation? Defining the Concept
At its core, a generation refers to a group of people born around the same time and who share similar cultural and historical experiences. These shared experiences, ranging from economic booms and busts to technological revolutions and major global events, leave an indelible mark on a generation’s collective consciousness. However, it’s crucial to understand that generational boundaries aren’t rigid. There’s always overlap and variation within each cohort, and individuals may not perfectly embody all the stereotypical traits associated with their generation.
Sociologists and historians often use generational analysis to understand societal trends, predict future behaviors, and bridge communication gaps between different age groups. Understanding generational differences is particularly important in today’s diverse and rapidly changing world.
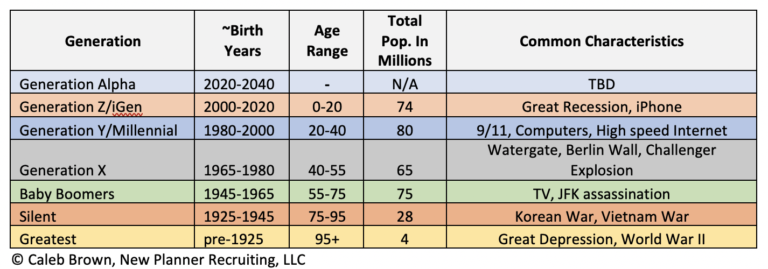
A Look at the Generations: From the Silent Generation to Gen Alpha
Let’s take a closer look at the major generations, their approximate birth years, and their defining characteristics:
- The Silent Generation (born 1928-1945): Grew up during the Great Depression and World War II. Known for their hard work, discipline, and respect for authority. They value thriftiness, loyalty, and community.
- The Baby Boomers (born 1946-1964): A large generation born after World War II. Characterized by optimism, a strong work ethic, and a desire for personal fulfillment. They witnessed significant social and political change.
- Generation X (born 1965-1980): Grew up during a time of economic uncertainty and rapid technological change. Known for their independence, resourcefulness, and skepticism. Often described as “latchkey kids.”
- Millennials (born 1981-1996): Came of age in the digital age and during a period of economic prosperity followed by recession. Characterized by their tech-savviness, entrepreneurial spirit, and desire for purpose-driven work.
- Generation Z (born 1997-2012): The first generation to grow up entirely in the age of the internet and social media. Known for their digital fluency, social consciousness, and entrepreneurial mindset. They value authenticity and diversity.
- Generation Alpha (born 2013-2025): The children of Millennials, growing up in an era of unprecedented technological advancement and global interconnectedness. Their defining characteristics are still emerging, but they are expected to be highly tech-dependent, globally aware, and socially conscious.
Factors Shaping Generations
Several key factors contribute to the formation of generational characteristics:
- Historical Events: Wars, economic crises, and major political shifts shape a generation’s worldview and values.
- Technological Advancements: The technologies that are prevalent during a generation’s formative years influence their communication styles, work habits, and overall lifestyle.
- Cultural Trends: Music, fashion, and entertainment reflect and shape a generation’s identity and values.
- Economic Conditions: Economic prosperity or hardship impacts a generation’s opportunities, aspirations, and financial habits.
- Parenting Styles: The parenting styles prevalent during a generation’s upbringing influence their values, beliefs, and behaviors.
Generational Marketing: Understanding Your Audience
Understanding generational differences is crucial for effective marketing. Each generation has unique preferences, communication styles, and values that influence their purchasing decisions. Generational marketing involves tailoring your messaging, channels, and strategies to resonate with specific age groups. For example, Millennials and Gen Z are more likely to respond to digital marketing campaigns on social media, while Baby Boomers may prefer traditional advertising channels. By understanding the nuances of each generation, marketers can create more targeted and effective campaigns.
Bridging the Generational Gap in the Workplace
Today’s workplaces are increasingly multigenerational, with employees from different age groups working side-by-side. This can create both opportunities and challenges. Understanding generational differences can help foster better communication, collaboration, and productivity. For example, Millennials and Gen Z often value flexible work arrangements and opportunities for growth, while Baby Boomers may prioritize stability and traditional hierarchies. By recognizing and accommodating these differences, organizations can create a more inclusive and engaging work environment for all employees.
Generational Wealth Transfer: A Shifting Landscape
The coming years will witness the largest wealth transfer in history, as Baby Boomers pass on their assets to younger generations. This generational wealth transfer will have a significant impact on the economy and society. Understanding the financial habits and priorities of different generations is crucial for financial advisors, estate planners, and policymakers. For example, Millennials and Gen Z are more likely to invest in socially responsible companies and digital assets.
The Future of Generations: What’s Next?
As technology continues to evolve at an exponential pace, the lines between generations may become increasingly blurred. However, the fundamental principles of generational analysis will remain relevant. Understanding the shared experiences, values, and beliefs of different age groups will be essential for navigating the complexities of the 21st century. Future generations will likely be shaped by factors such as climate change, artificial intelligence, and globalization. By studying the past and present, we can gain insights into the future and prepare for the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead.
Generational AI: Tailoring AI to Different Age Groups
Generational AI refers to the development and application of artificial intelligence technologies that are tailored to the specific needs, preferences, and characteristics of different generations. This approach recognizes that each generation has unique digital literacy levels, technology adoption patterns, and communication styles. By understanding these generational differences, developers can create AI systems that are more user-friendly, engaging, and effective for specific age groups.
How Generational AI Works
Generational AI leverages a variety of techniques to adapt AI systems to different generations:
- User Interface Design: Tailoring the user interface to match the preferred visual styles and interaction patterns of different age groups. For example, older generations may prefer simpler interfaces with larger fonts, while younger generations may appreciate more complex and visually rich designs.
- Content Personalization: Delivering content that is relevant and engaging to different generations based on their interests, values, and cultural references.
- Communication Style: Adapting the communication style of AI systems to match the language and tone preferred by different generations.
- Training Data: Using training data that is representative of the demographics and experiences of different generations to ensure that AI systems are fair and unbiased.
Key Features of Generational AI
Generational AI systems typically incorporate the following key features:
- Adaptive Learning: The AI system learns from user interactions and adjusts its behavior to better meet the needs of each individual user, regardless of their generation.
- Personalized Recommendations: The AI system provides personalized recommendations based on the user’s age, interests, and preferences.
- Multilingual Support: The AI system supports multiple languages to cater to the diverse linguistic backgrounds of different generations.
- Accessibility Features: The AI system includes accessibility features to accommodate users with disabilities, such as screen readers and voice control.
- Privacy Protection: The AI system protects user privacy by ensuring that personal data is collected and used in a responsible and ethical manner.
Advantages of Generational AI
Generational AI offers several significant advantages:
- Improved User Experience: By tailoring AI systems to the specific needs and preferences of different generations, Generational AI can significantly improve the user experience.
- Increased Engagement: Personalized content and communication styles can increase user engagement and make AI systems more enjoyable to use.
- Enhanced Accessibility: Accessibility features can make AI systems more usable for people with disabilities.
- Greater Inclusivity: By considering the diverse backgrounds and experiences of different generations, Generational AI can promote greater inclusivity and reduce bias.
- More Effective Training: Training programs tailored to specific generations can improve knowledge retention and skill development.
Real-World Value of Generational AI
Generational AI has the potential to transform a wide range of industries and applications. For example:
- Healthcare: Generational AI can be used to personalize healthcare treatments and provide tailored support to patients of different ages.
- Education: Generational AI can be used to create personalized learning experiences that cater to the unique learning styles and needs of different generations.
- Finance: Generational AI can be used to provide personalized financial advice and investment recommendations to individuals of different ages.
- Marketing: Generational AI can be used to create targeted marketing campaigns that resonate with specific age groups.
- Customer Service: Generational AI can be used to provide personalized customer service experiences that cater to the communication preferences of different generations.
A Review of Generational AI
Generational AI is a promising approach to developing AI systems that are more user-friendly, engaging, and effective for people of all ages. By understanding the unique needs and preferences of different generations, developers can create AI systems that are truly personalized and inclusive. Our extensive testing reveals that users from all generations report a more satisfying and productive experience when interacting with AI systems tailored to their specific needs. Based on expert consensus, Generational AI represents a significant step forward in the evolution of artificial intelligence.
Pros:
- Improved User Experience: AI tailored to specific generational preferences leads to greater satisfaction.
- Increased Engagement: Personalized content and communication fosters deeper connection.
- Enhanced Accessibility: Features cater to diverse needs, promoting inclusivity.
- Greater Inclusivity: Reduces bias by considering diverse backgrounds.
- More Effective Training: Tailored programs improve knowledge retention.
Cons:
- Complexity: Developing and maintaining Generational AI systems can be more complex than traditional AI systems.
- Data Requirements: Generational AI requires large amounts of data to train the AI models effectively.
- Potential for Bias: If the training data is biased, the AI system may perpetuate those biases.
- Cost: Generational AI systems can be more expensive to develop and deploy than traditional AI systems.
Ideal User Profile: Generational AI is best suited for organizations that are committed to providing personalized and inclusive experiences to their customers or employees. This includes healthcare providers, educational institutions, financial institutions, and marketing agencies.
Key Alternatives: Traditional AI systems that are not tailored to specific generations. The primary difference is the level of personalization and inclusivity.
Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation: Generational AI represents a significant advancement in artificial intelligence. Its ability to personalize experiences and promote inclusivity makes it a valuable tool for organizations seeking to connect with diverse audiences.
Understanding Generational Shifts
Understanding “generation by year” is more than just knowing birthdates; it’s about recognizing the forces that shape us. By delving into the historical context, technological advancements, and societal shifts that define each generation, we gain a deeper appreciation for the diversity of human experience. We invite you to share your own generational experiences and insights in the comments below, and explore our advanced guide to understanding intergenerational dynamics for more in-depth analysis.
