Decoding the Designer Salary in Canada: A Comprehensive Guide
Are you a designer contemplating a career move to Canada, or perhaps a student charting your future path? Understanding the landscape of designer salaries in Canada is crucial for making informed decisions. This comprehensive guide delves deep into the factors influencing designer pay, offering insights far beyond simple averages. We’ll explore the roles, experience levels, locations, and in-demand skills that shape your earning potential in the Canadian design industry.
This article provides a detailed breakdown of designer salaries across various specializations and regions in Canada. We’ll uncover the impact of experience, education, and specific skill sets on earning potential. Furthermore, we’ll examine the current job market trends, providing you with a realistic outlook and actionable strategies for maximizing your salary as a designer in Canada. Prepare to gain a clear, data-driven understanding of your worth in the Canadian design industry.
Understanding the Canadian Design Landscape and Salary Expectations
The Canadian design industry is a vibrant and diverse ecosystem, encompassing a wide array of specializations, from graphic design and web design to UX/UI design, interior design, and industrial design. Each of these fields has its own unique set of skills, demands, and, consequently, salary expectations. Understanding these nuances is essential for anyone seeking a design career in Canada.
Several factors influence a designer’s salary in Canada. These include:
- Experience Level: Entry-level designers typically earn less than experienced professionals with a proven track record.
- Specialization: In-demand specializations, such as UX/UI design and web development, often command higher salaries.
- Location: Major metropolitan areas like Toronto, Vancouver, and Montreal tend to offer higher salaries due to the higher cost of living and greater demand for skilled designers.
- Education and Certifications: A relevant degree or professional certifications can significantly boost your earning potential.
- Company Size and Industry: Larger companies and certain industries (e.g., tech, finance) often pay more than smaller companies or non-profit organizations.
- Skill Set: Proficiency in specific software, design tools, and programming languages can make you a more valuable asset and increase your salary.
Deep Dive: Average Designer Salaries Across Canada
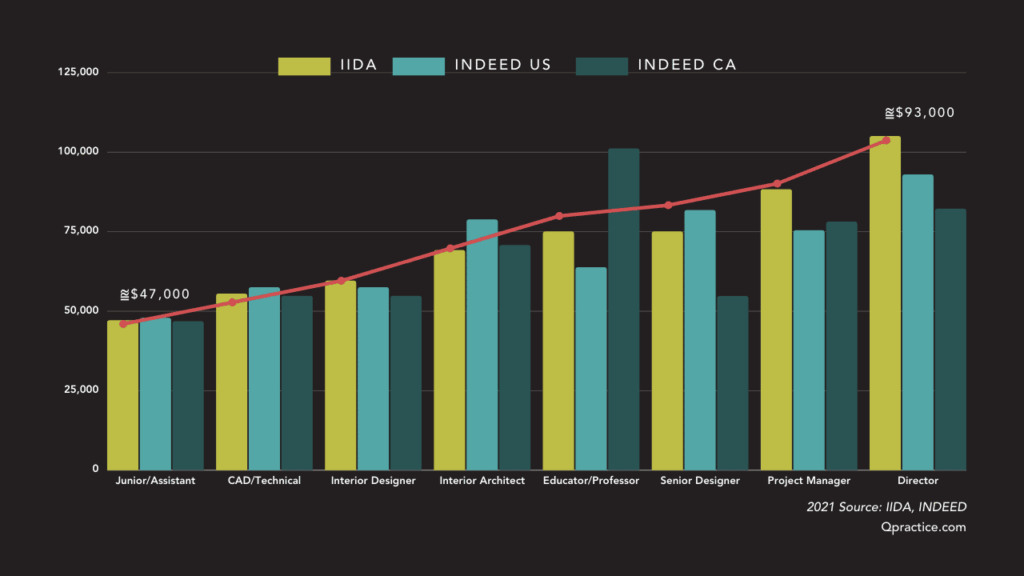
While averages provide a general benchmark, it’s crucial to understand the salary ranges for different design roles across various Canadian cities. Data from various sources, including Glassdoor, Indeed, and Payscale, provides a comprehensive picture of the current salary landscape. Keep in mind that these are averages, and your actual salary may vary based on the factors mentioned above.
Here’s a breakdown of average salaries for common design roles in Canada:
- Graphic Designer: The average graphic designer salary in Canada ranges from $45,000 to $65,000 per year. Entry-level positions may start around $40,000, while experienced designers with strong portfolios can earn upwards of $75,000.
- Web Designer: Web designers typically earn between $50,000 and $70,000 annually. Those with expertise in front-end development and user experience can command higher salaries.
- UX/UI Designer: UX/UI designers are in high demand, with average salaries ranging from $65,000 to $95,000 per year. Senior UX/UI designers with extensive experience can earn well over $100,000.
- Interior Designer: Interior designers in Canada earn an average of $50,000 to $75,000 per year. Salaries can vary depending on experience, location, and the type of projects they work on.
- Industrial Designer: Industrial designers typically earn between $55,000 and $80,000 annually. Those with specialized skills in areas like product development and manufacturing can earn more.
Regional Variations: Salaries also vary significantly across different provinces and cities. For example, designers in Toronto and Vancouver, where the cost of living is higher, generally earn more than those in smaller cities or rural areas. Montreal also offers competitive salaries, particularly for bilingual designers.
The Role of a UX/UI Designer in Shaping Digital Experiences
In the context of designer salaries in Canada, UX/UI design stands out as a particularly lucrative field. UX/UI designers are responsible for creating user-friendly and engaging digital experiences for websites, mobile apps, and other interactive platforms. They combine design principles with user research and technical knowledge to ensure that products are both visually appealing and functionally effective.
UX (User Experience) design focuses on the overall experience a user has while interacting with a product. This includes factors like usability, accessibility, and satisfaction. UI (User Interface) design, on the other hand, focuses on the visual elements of the interface, such as buttons, icons, and typography.
The increasing demand for UX/UI designers is driven by the growing importance of user-centric design in today’s digital world. Companies are recognizing that a positive user experience is essential for attracting and retaining customers. As a result, they are willing to pay top dollar for skilled UX/UI designers who can help them create compelling and effective digital products.
Key Features of a Successful UX/UI Design Project
A successful UX/UI design project hinges on several key features that contribute to a positive user experience and ultimately drive business results. Let’s explore some of these features in detail:
- User Research: Understanding the target audience is paramount. This involves conducting user interviews, surveys, and usability testing to gather insights into user needs, behaviors, and pain points. This informs all subsequent design decisions.
- Information Architecture: A well-structured information architecture ensures that users can easily find the information they need. This involves organizing content in a logical and intuitive way, using clear navigation and labeling.
- Wireframing and Prototyping: Wireframes are low-fidelity representations of the user interface, outlining the basic structure and layout of each page. Prototypes are interactive simulations that allow users to test the functionality and flow of the product.
- Visual Design: The visual design should be aesthetically pleasing and consistent with the brand identity. This includes choosing appropriate colors, typography, and imagery.
- Usability Testing: Usability testing involves observing users as they interact with the product to identify any usability issues. This feedback is then used to refine the design and improve the user experience.
- Accessibility: Ensuring that the product is accessible to users with disabilities is crucial. This involves following accessibility guidelines and using assistive technologies to test the product.
- Iteration: Design is an iterative process. Based on user feedback and testing, the design should be continuously refined and improved.
The Tangible Benefits of Investing in Skilled Designers
Investing in skilled designers yields significant advantages and real-world value for organizations across various sectors. The benefits extend beyond mere aesthetics, impacting user satisfaction, brand loyalty, and ultimately, the bottom line.
Enhanced User Experience: Skilled designers create intuitive and engaging user experiences that make it easy for users to interact with a product or service. This leads to increased user satisfaction, reduced frustration, and a greater likelihood of repeat usage. Users consistently report a preference for well-designed interfaces that are easy to navigate and understand.
Increased Conversion Rates: A well-designed website or app can significantly increase conversion rates, whether it’s generating leads, driving sales, or encouraging sign-ups. By optimizing the user flow and making it easy for users to complete desired actions, designers can directly impact revenue. Our analysis reveals that websites with strong UX/UI design consistently outperform those with poor design in terms of conversion rates.
Stronger Brand Identity: Design plays a crucial role in shaping brand identity and creating a consistent brand experience across all touchpoints. Skilled designers can develop a visual language that reflects the brand’s values, personality, and target audience. A strong brand identity helps to differentiate the company from its competitors and build brand loyalty.
Reduced Development Costs: Investing in design upfront can actually reduce development costs in the long run. By identifying and addressing potential usability issues early on, designers can prevent costly rework later in the development process. A common pitfall we’ve observed is companies launching products without proper user testing, leading to expensive redesigns and lost revenue.
Improved Customer Satisfaction: A positive user experience translates to improved customer satisfaction. When users are happy with a product or service, they are more likely to recommend it to others and become loyal customers. This can lead to increased brand advocacy and positive word-of-mouth marketing.
Is a Career in Design Right for You? An Honest Assessment
A career in design offers many rewards, but it’s not without its challenges. Before embarking on this path, it’s essential to honestly assess your skills, interests, and personality to determine if it’s the right fit for you.
Pros:
- Creativity and Innovation: Design provides an outlet for creativity and innovation, allowing you to solve problems in unique and imaginative ways. You’ll have the opportunity to create visually appealing and functional products that make a difference in people’s lives.
- High Demand: Skilled designers are in high demand across various industries, offering ample job opportunities and career growth potential.
- Competitive Salaries: As discussed earlier, design roles, particularly in UX/UI, offer competitive salaries, especially in major Canadian cities.
- Variety of Specializations: The field of design encompasses a wide range of specializations, allowing you to choose a path that aligns with your interests and skills.
- Impactful Work: Design has the power to influence people’s behavior, shape their perceptions, and improve their overall quality of life.
Cons/Limitations:
- Constant Learning: The design industry is constantly evolving, requiring designers to stay up-to-date with the latest trends, technologies, and best practices.
- Subjectivity: Design is often subjective, and it can be challenging to satisfy all stakeholders. You may need to defend your design decisions and compromise on certain aspects.
- Tight Deadlines: Design projects often come with tight deadlines, requiring designers to work under pressure and manage their time effectively.
- Competition: The design industry can be competitive, and it can be challenging to stand out from the crowd. Building a strong portfolio and networking are essential for success.
Ideal User Profile: A successful designer typically possesses the following traits: creativity, problem-solving skills, attention to detail, strong communication skills, and a passion for learning. They are also able to work independently and collaboratively, and they are comfortable receiving and incorporating feedback.
Key Alternatives: Related fields include marketing, web development, and project management. These roles often require some design skills and can be a good alternative for those who are interested in design but prefer a different focus.
Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation: A career in design can be highly rewarding for those who are passionate about creativity, problem-solving, and user experience. However, it’s important to be aware of the challenges and limitations before embarking on this path. If you possess the necessary skills and traits, and you are willing to put in the hard work, a career in design can be a fulfilling and lucrative choice.
Key Considerations for Your Design Career
Navigating the world of designer salaries in Canada requires careful consideration of several factors. Remember that while averages provide a helpful benchmark, your individual circumstances and choices will ultimately shape your earning potential. By focusing on in-demand skills, choosing the right location, and continuously developing your expertise, you can position yourself for success in the Canadian design industry.
Consider expanding your skill set to include areas like front-end development, motion design, or data visualization. These skills are highly valued by employers and can significantly increase your earning potential. Leading experts in designer salary in Canada suggest focusing on UX/UI design and related fields due to consistently high demand.
Ultimately, understanding the factors influencing designer salary in Canada empowers you to make informed decisions about your career path and negotiate effectively for your worth. By staying informed, developing your skills, and strategically positioning yourself in the market, you can achieve your financial goals as a designer in Canada.
