The Harmonious Mind: Exploring OCD in Musicians and Its Impact on Creativity
The world of music often seems like a realm of boundless creativity and effortless expression. However, beneath the surface of captivating performances and meticulously crafted compositions, some musicians grapple with the challenges of Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD). This article delves into the complex relationship between musicians who are OCD, exploring how this condition can manifest in their lives and work, and examining its potential impact on their artistic endeavors. We aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of this often-misunderstood intersection, offering insights and resources for musicians and those who support them.
Understanding OCD: Beyond the Stereotypes
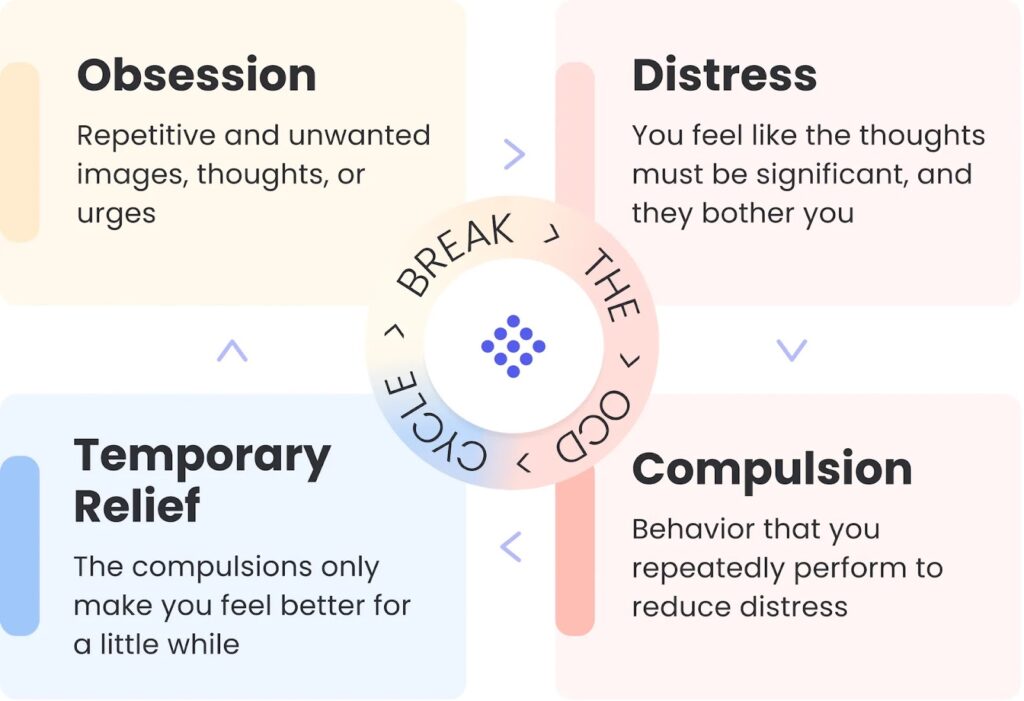
OCD is a mental health disorder characterized by persistent, intrusive thoughts (obsessions) that cause significant anxiety and distress. These obsessions often lead to repetitive behaviors or mental acts (compulsions) that individuals feel driven to perform in an attempt to neutralize the obsessions or prevent feared consequences. It’s crucial to understand that OCD is far more than just a preference for cleanliness or order; it’s a debilitating condition that can significantly interfere with daily functioning.
Common obsessions include:
- Fear of contamination
- Need for symmetry or order
- Aggressive or violent thoughts
- Religious obsessions (scrupulosity)
- Unwanted sexual thoughts
Compulsions can take many forms, such as:
- Excessive handwashing or cleaning
- Ordering or arranging objects in a specific way
- Checking things repeatedly (e.g., locks, appliances)
- Mental rituals (e.g., counting, praying)
- Seeking reassurance
The severity of OCD can vary greatly, with some individuals experiencing mild symptoms that have minimal impact on their lives, while others face significant impairment. Effective treatments for OCD include cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), particularly exposure and response prevention (ERP), and medication, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs).
The Unique Challenges Faced by Musicians with OCD
For musicians who are OCD, the condition can present unique challenges that intersect with the demands of their profession. The pursuit of perfection, the need for precision, and the pressure to perform can exacerbate OCD symptoms. The creative process itself, which often involves uncertainty and vulnerability, can also be triggering for individuals with OCD.
Here are some specific ways OCD can manifest in musicians:
- Obsessive focus on technical details: A musician might become fixated on achieving perfect intonation, rhythm, or articulation, spending excessive time practicing specific passages to the point of exhaustion.
- Compulsive practicing: The fear of making mistakes can lead to compulsive practicing rituals, where the musician feels compelled to repeat certain exercises or pieces countless times, even when they are already proficient.
- Contamination fears related to instruments: A musician might worry about germs or dirt on their instrument, leading to excessive cleaning or avoidance of sharing instruments.
- Symmetry and order compulsions related to sheet music or equipment: A musician might feel the need to arrange their sheet music or equipment in a specific way, becoming distressed if anything is out of place.
- Scrupulosity related to artistic expression: A musician might struggle with doubts about the morality or appropriateness of their creative choices, leading to self-censorship or anxiety about audience reactions.
The Potential Upsides: How OCD Can Fuel Creativity
While OCD can undoubtedly be a source of distress and impairment for musicians who are OCD, it’s also important to acknowledge the potential upsides. The intense focus, attention to detail, and drive for perfection that are characteristic of OCD can, in some cases, fuel creativity and lead to exceptional artistic achievements. Some musicians have reported that their OCD tendencies have helped them to:
- Develop exceptional technical skills: The compulsive practicing and attention to detail can result in a high level of technical proficiency.
- Create highly structured and meticulously crafted compositions: The need for order and symmetry can translate into complex and well-organized musical structures.
- Explore unconventional ideas: The obsessive nature of OCD can lead to a deep exploration of specific themes or concepts, resulting in unique and innovative works.
- Persevere through challenges: The determination and resilience that are often associated with OCD can help musicians overcome obstacles and achieve their artistic goals.
Notable Musicians Who Have Spoken About OCD
Several prominent musicians have publicly discussed their experiences with OCD, helping to raise awareness and reduce stigma. While it’s impossible to diagnose individuals without a proper evaluation, their stories offer valuable insights into the challenges and triumphs of living with OCD as a musician.
- David Beckham: While primarily known for his football career, Beckham has spoken openly about his OCD, which manifests in his need for order and symmetry.
- Howie Mandel: The comedian and television personality has been a vocal advocate for mental health awareness, sharing his experiences with OCD and anxiety.
These are just a few examples, and it’s likely that many other musicians struggle with OCD in silence. By sharing their stories, these individuals help to break down the stigma surrounding mental health and encourage others to seek help.
Treatment Options and Coping Strategies for Musicians with OCD
Effective treatment is available for musicians who are OCD. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), particularly exposure and response prevention (ERP), is considered the gold standard treatment for OCD. ERP involves gradually exposing individuals to their feared obsessions while preventing them from engaging in their compulsive behaviors. This helps them to learn that their anxiety will eventually subside without the need for compulsions.
Medication, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), can also be helpful in managing OCD symptoms. SSRIs work by increasing the levels of serotonin in the brain, which can help to reduce anxiety and obsessive thoughts.
In addition to professional treatment, there are several coping strategies that musicians with OCD can use to manage their symptoms:
- Mindfulness and meditation: These practices can help musicians to become more aware of their thoughts and feelings without judgment, reducing the power of obsessions.
- Self-compassion: Practicing self-compassion can help musicians to be kinder to themselves and to accept their imperfections.
- Setting realistic goals: Setting achievable goals can help musicians to avoid feeling overwhelmed by their perfectionistic tendencies.
- Seeking support from peers: Connecting with other musicians who have OCD can provide a sense of community and understanding.
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle: Getting enough sleep, eating a balanced diet, and exercising regularly can help to reduce stress and improve overall well-being.
The Role of Music Therapy in Managing OCD Symptoms
Music therapy can be a valuable tool for musicians who are OCD. It provides a creative outlet for expressing emotions and processing difficult experiences. Music therapy can also help musicians to develop coping skills and improve their self-esteem.
Here are some ways music therapy can be beneficial for musicians with OCD:
- Reducing anxiety and stress: Music has a calming effect on the nervous system, which can help to reduce anxiety and stress.
- Improving emotional regulation: Music therapy can help musicians to identify and express their emotions in a healthy way.
- Increasing self-awareness: Music therapy can help musicians to gain a deeper understanding of themselves and their motivations.
- Developing coping skills: Music therapy can teach musicians coping skills for managing their OCD symptoms.
- Enhancing self-esteem: Music therapy can help musicians to feel more confident and capable.
A qualified music therapist can tailor treatment to meet the specific needs of each individual.
The Importance of Support and Understanding
For musicians who are OCD, having a strong support system is crucial. Family, friends, and colleagues can play a vital role in providing encouragement, understanding, and practical assistance.
Here are some ways to support a musician with OCD:
- Educate yourself about OCD: Understanding the nature of OCD can help you to be more empathetic and supportive.
- Listen without judgment: Create a safe space for the musician to share their thoughts and feelings without fear of criticism.
- Encourage them to seek professional help: Offer to help them find a therapist or psychiatrist who specializes in OCD.
- Be patient and understanding: Remember that OCD is a chronic condition that can take time to manage.
- Celebrate their successes: Acknowledge and appreciate their accomplishments, no matter how small.
The Fine Line Between Perfectionism and OCD in Music
It’s important to distinguish between healthy perfectionism and OCD. While perfectionism can drive musicians to strive for excellence, OCD involves intrusive thoughts and compulsive behaviors that cause significant distress and impairment. The key difference lies in the level of control and the impact on daily functioning. A healthy perfectionist can let go of their pursuit of perfection when necessary, while someone with OCD feels compelled to engage in compulsive behaviors despite the negative consequences.
Musicians who are OCD often struggle with this distinction, as the pursuit of perfection is often seen as a desirable trait in the music world. However, it’s essential to recognize when perfectionism crosses the line into OCD and to seek help if necessary.
Finding Harmony: Thriving as a Musician with OCD
Living with OCD as a musician presents unique challenges, but it’s also possible to thrive and achieve artistic success. By seeking appropriate treatment, developing coping strategies, and building a strong support system, musicians who are OCD can manage their symptoms and harness their creative potential. The journey may not always be easy, but the rewards of artistic expression and personal growth are well worth the effort. If you’re a musician struggling with OCD, remember that you’re not alone, and help is available. Embrace your unique perspective, find your voice, and share your music with the world. Consider exploring online communities and forums dedicated to musicians and mental health, as these platforms can provide invaluable peer support and shared experiences. Seeking professional guidance from therapists specializing in creative arts populations can also offer tailored strategies for managing OCD within the context of a musical career.
