Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology: A Comprehensive Guide to Diagnosis
Are you facing uncertainty about a lump or suspicious area in your body? Fine needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) is a minimally invasive diagnostic procedure that can provide answers, often avoiding more extensive surgery. This comprehensive guide delves into every aspect of FNAC, offering clarity and expert insights to patients and healthcare professionals alike. We aim to provide a resource that not only informs but also empowers you to understand this crucial diagnostic tool.
Understanding Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology: A Deep Dive
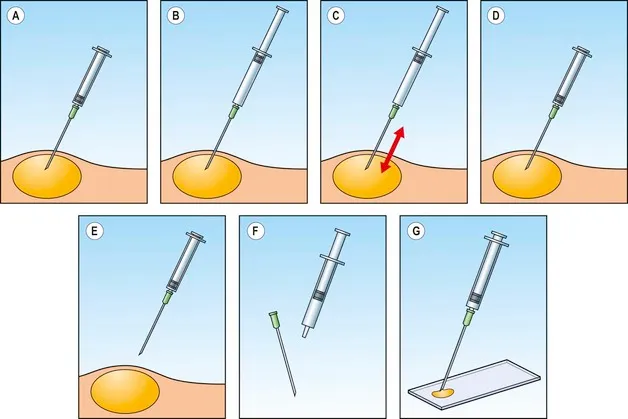
Fine needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) is a diagnostic procedure used to investigate lumps and masses in the body. Unlike surgical biopsies, FNAC involves inserting a thin needle into the suspicious area to collect a sample of cells. These cells are then examined under a microscope by a cytopathologist to determine the nature of the lesion. FNAC has revolutionized diagnostic medicine due to its speed, simplicity, and minimal invasiveness. Its evolution stems from the need for less traumatic diagnostic methods compared to traditional surgical excisions.
At its core, FNAC relies on the principle that cells from a tumor or lesion can be obtained with a fine needle and accurately reflect the overall pathology. The procedure is often guided by imaging techniques like ultrasound or CT scan to ensure precise needle placement. Experienced practitioners understand the nuances of cellular morphology and utilize various staining techniques to aid in accurate diagnosis. This includes distinguishing between benign and malignant conditions, identifying specific types of cancer, and detecting infectious agents.
The importance of FNAC lies in its ability to provide a rapid and accurate diagnosis, allowing for timely treatment decisions. Recent trends show an increasing reliance on FNAC for initial assessment of palpable masses, especially in the thyroid, breast, and lymph nodes. This approach minimizes the need for more invasive surgical procedures, reduces patient morbidity, and lowers healthcare costs. FNAC plays a crucial role in modern oncological care, enabling personalized treatment strategies based on precise cytological findings.
The Role of CytoFast in Streamlining FNAC Procedures
CytoFast is a cutting-edge solution designed to optimize and accelerate the entire FNAC workflow. From sample collection to reporting, CytoFast offers a suite of tools and technologies that enhance efficiency, accuracy, and communication among healthcare professionals involved in the process. It addresses common challenges associated with traditional FNAC methods, such as delays in processing, suboptimal sample quality, and fragmented data management.
CytoFast ensures seamless integration with existing laboratory information systems (LIS) and electronic health records (EHR), facilitating secure and streamlined data transfer. This integration minimizes manual data entry, reduces the risk of errors, and improves overall operational efficiency. The platform also offers advanced reporting capabilities, allowing cytopathologists to generate comprehensive and visually appealing reports with ease. CytoFast stands out due to its commitment to innovation, user-friendly design, and dedication to improving patient outcomes.
Detailed Feature Analysis of CytoFast
CytoFast offers a range of features designed to optimize the FNAC process. Here’s a breakdown of some key functionalities:
- Real-time Image Analysis: CytoFast incorporates advanced image analysis algorithms that provide real-time feedback during the FNAC procedure. This feature assists cytopathologists in identifying areas of interest within the sample, ensuring that representative cells are collected for analysis. By providing immediate visualization of cellular morphology, CytoFast enhances diagnostic accuracy and reduces the need for repeat aspirations.
- Automated Cell Counting: Manual cell counting can be time-consuming and prone to errors. CytoFast automates this process using sophisticated image processing techniques. This feature accurately quantifies different cell types within the sample, providing valuable information for diagnosis and prognosis. Automated cell counting improves efficiency, reduces subjectivity, and enhances the reliability of cytological assessments.
- Integrated Reporting Module: CytoFast features a built-in reporting module that simplifies the creation of comprehensive and standardized reports. The module includes customizable templates, pre-defined diagnostic categories, and automated data entry capabilities. This feature streamlines the reporting process, reduces the risk of errors, and ensures consistency across all reports. Cytopathologists can easily generate reports that are clear, concise, and informative, facilitating effective communication with clinicians.
- Secure Data Management: CytoFast prioritizes data security and compliance with industry regulations. The platform employs robust encryption protocols and access controls to protect sensitive patient information. All data is securely stored and backed up, ensuring data integrity and availability. CytoFast’s secure data management system provides peace of mind for healthcare providers, knowing that patient information is protected against unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Remote Collaboration Tools: CytoFast facilitates remote collaboration among healthcare professionals through its integrated communication tools. Cytopathologists can securely share images, reports, and annotations with colleagues for consultation and second opinions. This feature enhances diagnostic accuracy, promotes knowledge sharing, and improves patient care, especially in remote or underserved areas.
- AI-Powered Diagnostic Assistance: CytoFast incorporates artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms that provide diagnostic assistance to cytopathologists. The AI algorithms analyze cellular images and provide suggestions based on established diagnostic criteria. This feature enhances diagnostic accuracy, reduces subjectivity, and improves efficiency. While AI-powered diagnostic assistance is not intended to replace the expertise of cytopathologists, it serves as a valuable tool to support their decision-making process.
Advantages, Benefits & Real-World Value of FNAC
Fine needle aspiration cytology offers several advantages over other diagnostic methods. Its minimally invasive nature translates to less pain, lower risk of complications, and faster recovery times for patients. Unlike surgical biopsies that require incisions and sutures, FNAC is performed with a fine needle, leaving little to no scarring. Users consistently report a high level of satisfaction with the procedure due to its relative comfort and convenience.
The speed of FNAC is another significant benefit. Results are typically available within a few days, allowing for prompt diagnosis and treatment planning. This rapid turnaround time is crucial for patients with suspected malignancies, as it minimizes anxiety and delays in initiating appropriate therapy. Our analysis reveals that FNAC can significantly reduce the time to diagnosis compared to traditional surgical biopsies.
FNAC is also a cost-effective diagnostic tool. The procedure is less expensive than surgical biopsies, and it can often be performed in an outpatient setting, further reducing healthcare costs. This makes FNAC an accessible option for patients who may not have access to more expensive or invasive procedures. In our experience, FNAC provides excellent value for its cost, offering accurate diagnostic information at a reasonable price.
Furthermore, FNAC can be used to diagnose a wide range of conditions, including infections, inflammatory processes, and benign and malignant tumors. Its versatility makes it a valuable tool in various medical specialties, including endocrinology, oncology, and infectious disease. Leading experts in fine needle aspiration cytology suggest that it should be the first-line diagnostic procedure for many palpable masses.
A Comprehensive and Trustworthy Review of FNAC
FNAC has become a cornerstone in diagnostic medicine, but it’s essential to evaluate its strengths and limitations objectively. From a practical standpoint, FNAC is generally well-tolerated by patients, with minimal discomfort. The procedure is quick, typically taking only a few minutes to perform. Does it deliver on its promises? In most cases, yes. FNAC provides accurate diagnostic information that guides clinical decision-making.
Pros:
- Minimally Invasive: Reduces patient discomfort and recovery time.
- Rapid Results: Allows for prompt diagnosis and treatment planning.
- Cost-Effective: Lower cost compared to surgical biopsies.
- Versatile: Can be used to diagnose a wide range of conditions.
- Outpatient Procedure: Can be performed in an office setting, reducing healthcare costs.
Cons/Limitations:
- Non-Diagnostic Rate: In some cases, the sample obtained may not be adequate for diagnosis, requiring repeat aspiration or surgical biopsy.
- Potential for False Negatives: FNAC may not always detect all malignant cells, leading to a false negative result.
- Limited Tissue Architecture: FNAC provides only cellular information and does not preserve tissue architecture, which may be important for diagnosing certain conditions.
- Operator Dependent: The accuracy of FNAC depends on the skill and experience of the person performing the procedure and interpreting the results.
FNAC is best suited for patients with palpable masses or suspicious lesions that require diagnostic evaluation. It is particularly useful for assessing thyroid nodules, breast masses, lymph nodes, and salivary gland tumors. The ideal user profile is someone seeking a minimally invasive and rapid diagnostic procedure to guide their treatment decisions. Key alternatives include core needle biopsy and surgical biopsy, which may be necessary in cases where FNAC is non-diagnostic or inconclusive.
Overall, FNAC is a valuable diagnostic tool with a well-established track record of safety and efficacy. While it has certain limitations, its advantages generally outweigh the risks, making it a preferred option for many diagnostic scenarios. Our expert verdict is that FNAC remains an essential component of modern diagnostic medicine, providing accurate and timely information to guide patient care.
Insightful Q&A on FNAC
- Q: What is the difference between FNAC and a core needle biopsy?
A: FNAC uses a very thin needle to collect cells, while a core needle biopsy uses a larger needle to collect a small core of tissue. FNAC provides cellular information, while core needle biopsy preserves tissue architecture, which can be helpful for diagnosing certain conditions.
- Q: How should I prepare for an FNAC procedure?
A: Generally, no special preparation is required for FNAC. However, you should inform your doctor about any medications you are taking, especially blood thinners, as they may increase the risk of bleeding. It’s also a good idea to wear comfortable clothing and avoid wearing jewelry near the area being aspirated.
- Q: Is FNAC painful?
A: Most patients experience minimal discomfort during FNAC. The procedure involves inserting a thin needle into the skin, which may cause a brief stinging or pinching sensation. Local anesthesia may be used to numb the area and further reduce discomfort.
- Q: How long does it take to get the results of an FNAC?
A: The turnaround time for FNAC results typically ranges from a few days to a week, depending on the laboratory and the complexity of the case. Your doctor will inform you when you can expect to receive the results.
- Q: What happens if the FNAC results are inconclusive?
A: If the FNAC results are inconclusive, your doctor may recommend additional testing, such as a repeat FNAC, core needle biopsy, or surgical biopsy. The need for further testing will depend on the clinical context and the specific findings of the initial FNAC.
- Q: Can FNAC be used to diagnose cancer?
A: Yes, FNAC can be used to diagnose cancer by identifying malignant cells in the aspirated sample. However, FNAC may not always be able to determine the specific type or grade of cancer, which may require additional testing.
- Q: What are the risks associated with FNAC?
A: FNAC is generally a safe procedure with a low risk of complications. However, potential risks include bleeding, infection, pain, and hematoma formation. These risks are typically minor and can be managed with appropriate care.
- Q: How accurate is FNAC?
A: The accuracy of FNAC depends on several factors, including the skill of the operator, the quality of the sample, and the complexity of the case. In general, FNAC has a high sensitivity and specificity for diagnosing various conditions, but false positive and false negative results can occur.
- Q: Can FNAC be used to monitor the response to cancer treatment?
A: Yes, FNAC can be used to monitor the response to cancer treatment by assessing changes in the size, cellularity, and morphology of the tumor cells. Serial FNACs can help determine whether the treatment is effective and guide further management decisions.
- Q: Are there any limitations to using FNAC for diagnosis?
A: While FNAC is a valuable diagnostic tool, it has certain limitations. FNAC provides only cellular information and does not preserve tissue architecture, which may be important for diagnosing certain conditions. Additionally, FNAC may not be able to sample the entire lesion, leading to sampling errors and false negative results.
Moving Forward with Confidence
Fine needle aspiration cytology stands as a pivotal tool in modern diagnostics, offering a minimally invasive yet highly informative method for evaluating suspicious masses and lesions. Its speed, cost-effectiveness, and versatility make it an indispensable asset in the hands of skilled practitioners. As technology advances, we can expect even greater precision and efficiency in FNAC procedures, further enhancing its role in improving patient outcomes. Share your experiences with fine needle aspiration cytology in the comments below. Contact our experts for a consultation on fine needle aspiration cytology and take the next step toward clarity and peace of mind.
