What is 6-48 Thread? Your Definitive Guide
If you’ve ever encountered the term “6-48 thread” and found yourself scratching your head, you’re not alone. This seemingly simple designation refers to a specific type of screw thread, but understanding its nuances is crucial in various fields, from firearms to precision instruments. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of 6-48 threads, exploring their dimensions, applications, advantages, and how they stack up against alternatives. We aim to provide you with the most in-depth and reliable information available, drawing on industry best practices and expert insights to ensure you gain a complete understanding of this vital component.
Understanding the Basics of Screw Threads
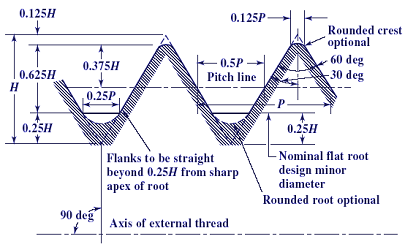
Before diving directly into the specifics of a 6-48 thread, it’s essential to grasp the fundamental concepts of screw threads in general. A screw thread is essentially a helical ridge wrapped around a cylinder or cone. This ridge, known as the thread, allows the screw to be driven into a material, creating a strong and secure fastening. Threads are characterized by several key parameters:
- Major Diameter: The largest diameter of the thread.
- Minor Diameter: The smallest diameter of the thread.
- Pitch: The distance between adjacent threads.
- Threads Per Inch (TPI): The number of threads per inch, which is the inverse of the pitch.
These parameters dictate the strength, holding power, and ease of installation of a screw. Different applications require different thread specifications, leading to a wide variety of thread sizes and types.
Decoding the 6-48 Thread Designation
The “6-48” designation refers to a specific Unified Thread Standard (UTS) screw thread. Let’s break down what each number signifies:
- 6: This number indicates the nominal size of the screw. In the UTS system, sizes are designated by numbers ranging from 0 to 12, with larger numbers indicating larger diameters. A size 6 screw has a major diameter of 0.1380 inches.
- 48: This number represents the threads per inch (TPI). In this case, there are 48 threads packed into each inch of the screw’s length. This is considered a fine thread.
Therefore, a 6-48 thread is a screw with a nominal size of 6 and 48 threads per inch. This combination creates a fine thread suitable for applications requiring precision and strong holding power in relatively thin materials.
Applications of 6-48 Threads
6-48 threads are commonly found in applications where a small, strong, and precise fastening is required. Some of the most common applications include:
- Firearms: Specifically, scope mounting screws on rifles. The fine thread provides a secure and vibration-resistant connection, crucial for maintaining accuracy.
- Electronics: Securing small components and housings in electronic devices. The small size of the 6-48 screw makes it ideal for compact electronics.
- Precision Instruments: Used in instruments requiring precise adjustments and secure fastening, such as measuring tools and optical equipment.
- Model Making: Hobbyists and model makers often employ 6-48 screws for assembling intricate models due to their small size and fine threads.
Advantages of Using 6-48 Threads
The popularity of 6-48 threads stems from several key advantages:
- High Holding Power: The fine thread provides a greater surface area for engagement, resulting in a stronger and more secure hold compared to coarser threads.
- Vibration Resistance: The tight thread pitch makes 6-48 screws less likely to loosen due to vibration, making them ideal for applications subject to movement or shock.
- Precision: The fine thread allows for precise adjustments and tightening, crucial in applications requiring accuracy and control.
- Compact Size: The small size of the 6-48 screw makes it suitable for applications where space is limited.
6-48 Thread vs. Other Common Thread Sizes
To fully appreciate the characteristics of a 6-48 thread, it’s helpful to compare it to other common thread sizes. Let’s consider a few examples:
6-32 Thread
A 6-32 thread has the same nominal size as a 6-48 thread but features a coarser thread pitch (32 threads per inch). This makes it easier to install and less prone to cross-threading. However, it offers less holding power and vibration resistance compared to a 6-48 thread.
8-32 Thread
An 8-32 thread is larger in diameter than a 6-48 thread and also has a coarser thread pitch. It provides greater overall strength but is not suitable for applications requiring a small and precise fastening.
4-40 Thread
A 4-40 thread is smaller in diameter than a 6-48 thread but has a similar thread pitch. It’s often used in applications where even smaller screws are required, but it offers less holding power than a 6-48 thread.
The choice between these thread sizes depends on the specific requirements of the application, considering factors such as size constraints, required holding power, and vibration resistance.
Materials Used for 6-48 Thread Screws
6-48 thread screws are available in a variety of materials, each offering different properties and suitable for different applications. Common materials include:
- Stainless Steel: Offers excellent corrosion resistance and is suitable for applications exposed to moisture or harsh environments.
- Carbon Steel: Provides high strength and is often used in applications where corrosion is not a major concern. Can be surface treated with coatings like black oxide for some corrosion resistance.
- Alloy Steel: Offers enhanced strength and toughness compared to carbon steel, suitable for demanding applications.
- Brass: Provides good corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity, often used in electrical applications.
- Titanium: Offers exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance, used in high-performance applications where weight is a critical factor.
The choice of material depends on the specific application requirements, considering factors such as strength, corrosion resistance, and cost.
Tools for Working with 6-48 Threads
Working with 6-48 threads requires specialized tools to ensure proper installation and prevent damage. Essential tools include:
- Screwdrivers: Precision screwdrivers with the correct tip size (usually a Phillips or flathead) are essential for driving 6-48 screws.
- Taps and Dies: Taps are used to create internal threads in a hole, while dies are used to create external threads on a rod or bolt. A 6-48 tap and die set is necessary for creating or repairing 6-48 threads.
- Thread Gauges: Used to verify the accuracy of thread dimensions, ensuring proper fit and function.
- Torque Wrenches: Essential for tightening 6-48 screws to the correct torque specification, preventing over-tightening or under-tightening. This is particularly important in applications where precise torque is critical, such as scope mounting.
Using the correct tools is crucial for ensuring proper installation and preventing damage to the screw or the mating component.
Expert Insights on 6-48 Thread in Firearms Scope Mounting
As mentioned earlier, 6-48 threads are commonly used for mounting scopes on firearms. This application demands high precision and reliability, as the scope must remain securely attached to the rifle to maintain accuracy. According to leading gunsmiths, the 6-48 thread size provides an excellent balance of strength and size for this purpose. The fine thread pitch ensures a secure and vibration-resistant connection, preventing the scope from loosening during recoil. Furthermore, the small size of the 6-48 screw allows for a compact and streamlined scope mounting system. Incorrect installation or using the wrong torque can lead to scope slippage and inaccuracy, underscoring the importance of proper technique and tools.
Real-World Examples of 6-48 Thread Applications
Beyond the specific use cases already mentioned, 6-48 threads find their way into various other applications where precision and small size are paramount. Consider the intricate mechanisms of a high-end wristwatch. Tiny 6-48 screws might be used to secure the delicate gears and components within the movement. Similarly, in the field of medical devices, where miniaturization is constantly pushing boundaries, 6-48 threads could be employed in surgical instruments or diagnostic equipment. These examples highlight the versatility of 6-48 threads in situations demanding reliable fastening in confined spaces.
Navigating the World of Miniature Fasteners: A Guide to 6-48 Thread
In conclusion, the 6-48 thread represents a specific and valuable fastening solution for applications demanding precision, strength, and a compact size. Its fine thread pitch provides exceptional holding power and vibration resistance, making it a popular choice in firearms, electronics, and precision instruments. Understanding the characteristics of 6-48 threads, along with the appropriate tools and materials, is essential for ensuring proper installation and optimal performance. Whether you’re a gunsmith mounting a scope, an electronics technician assembling a device, or a hobbyist building a model, mastering the intricacies of 6-48 threads will undoubtedly enhance your craftsmanship and ensure reliable results.
To further expand your understanding of fastener types and applications, explore our detailed guide on threadlocking compounds or contact our experts for a consultation on your specific needs. Understanding the nuances of threads like the 6-48 can significantly improve the quality and longevity of your projects.
